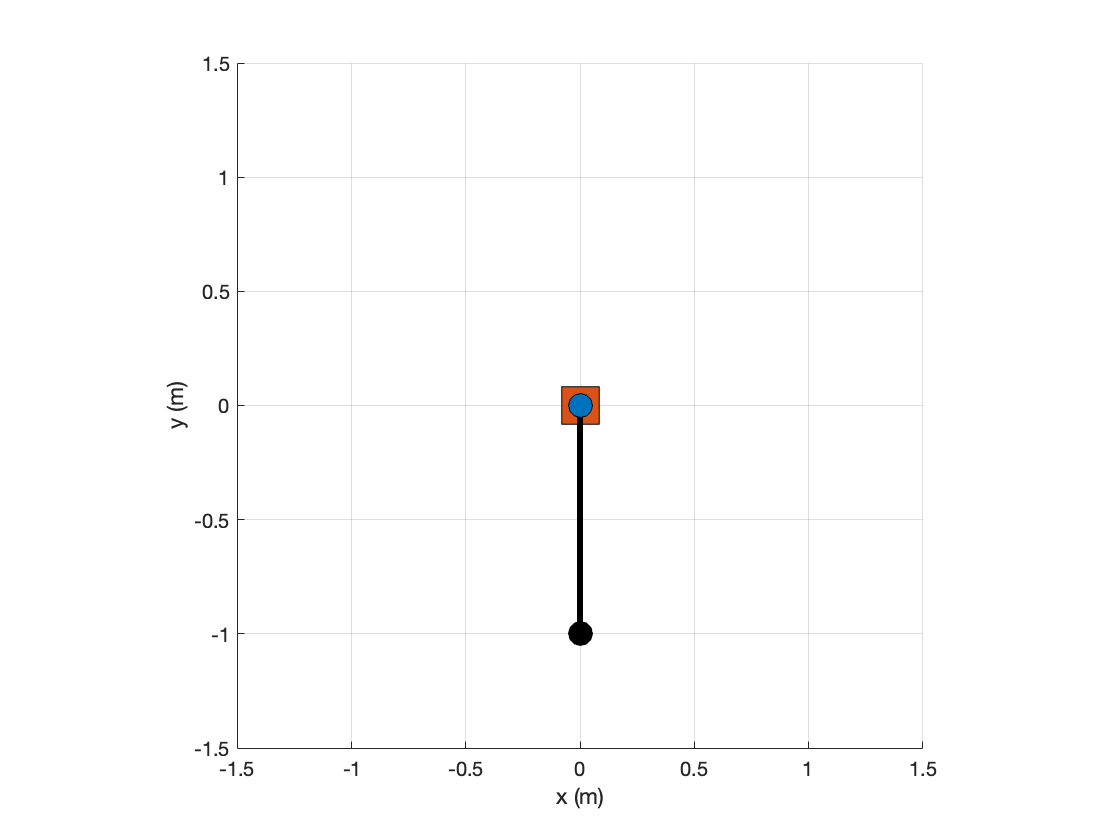
Cart-Pole
Cart-Pole robot is one frequently used example in academia. The geometric and inertial parameters are shown below:
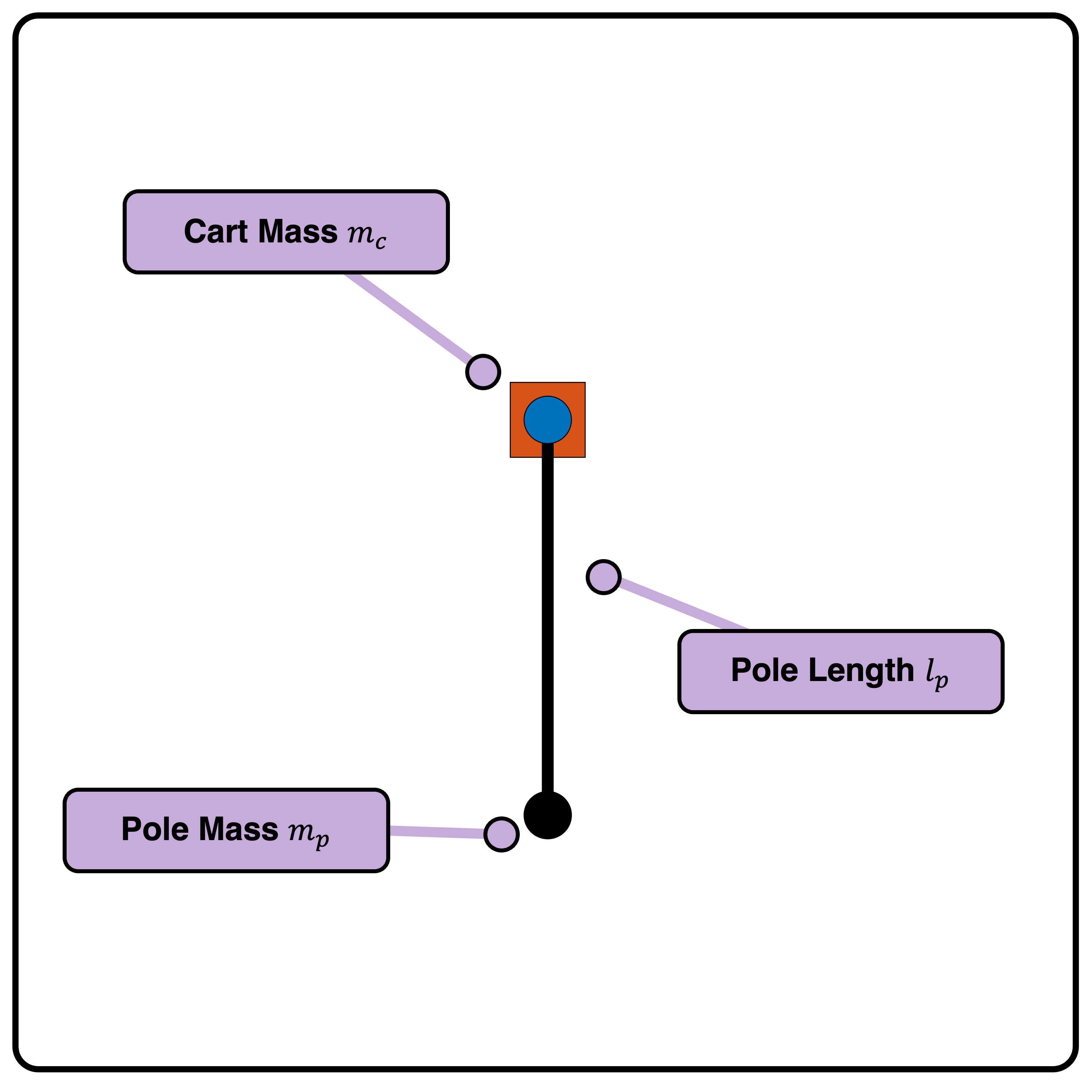
A cart with point mass \(m_c\).
A pole with length \(l_p\) and point mass \(m_p\) attached to the end of the pole.
Note that the system consists of point masses, i.e., the center of mass of each link is identical to the position of the mass. Moreover, the moment of inertia about the center of mass can be neglected.
Initial Configuration and Joint Parameters
Below, the robot in initial configuration with stationary coordinate frame \(\{S\}\) and origin \(\{O\}\) is shown:
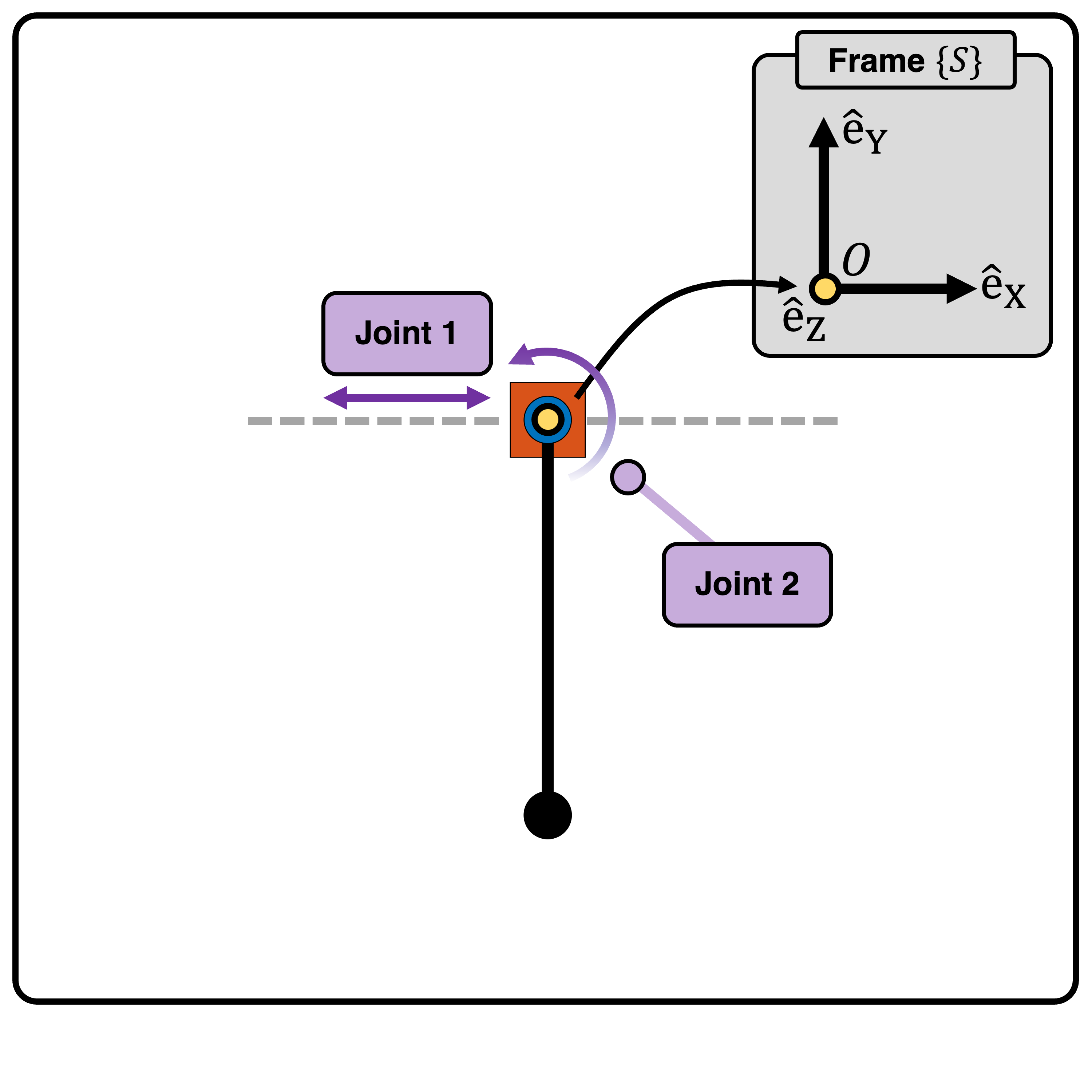
Joint |
Type |
Point on Joint Twist Axis (m) |
Joint Direction |
Joint Twist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Joint 1 |
Prismatic (2) |
(0, 0, 0) |
(1, 0, 0) |
(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) |
Joint 2 |
Revolute (1) |
(0, 0, 0) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1) |
Example code
To construct the cart-pole robot, run the following code:
% Geometric and Inertial Parameters of the cart-pole robot
mc = 1; % The mass of the cart
mp = 1; % The mass of the pole
lp = 1; % The length of the pole
% Construct the cart-pole robot and initialize
robot = CartPole( mc, mp, lp );
robot.init( )
% Attach the cart-pole robot to animation for visualization
anim = Animation( 'Dimension', 2, 'xLim', [-1.5,1.5], 'yLim', [-1.5,1.5]);
anim.init( )
anim.attachRobot( robot )
The output figure should look like this: