Franka Emika
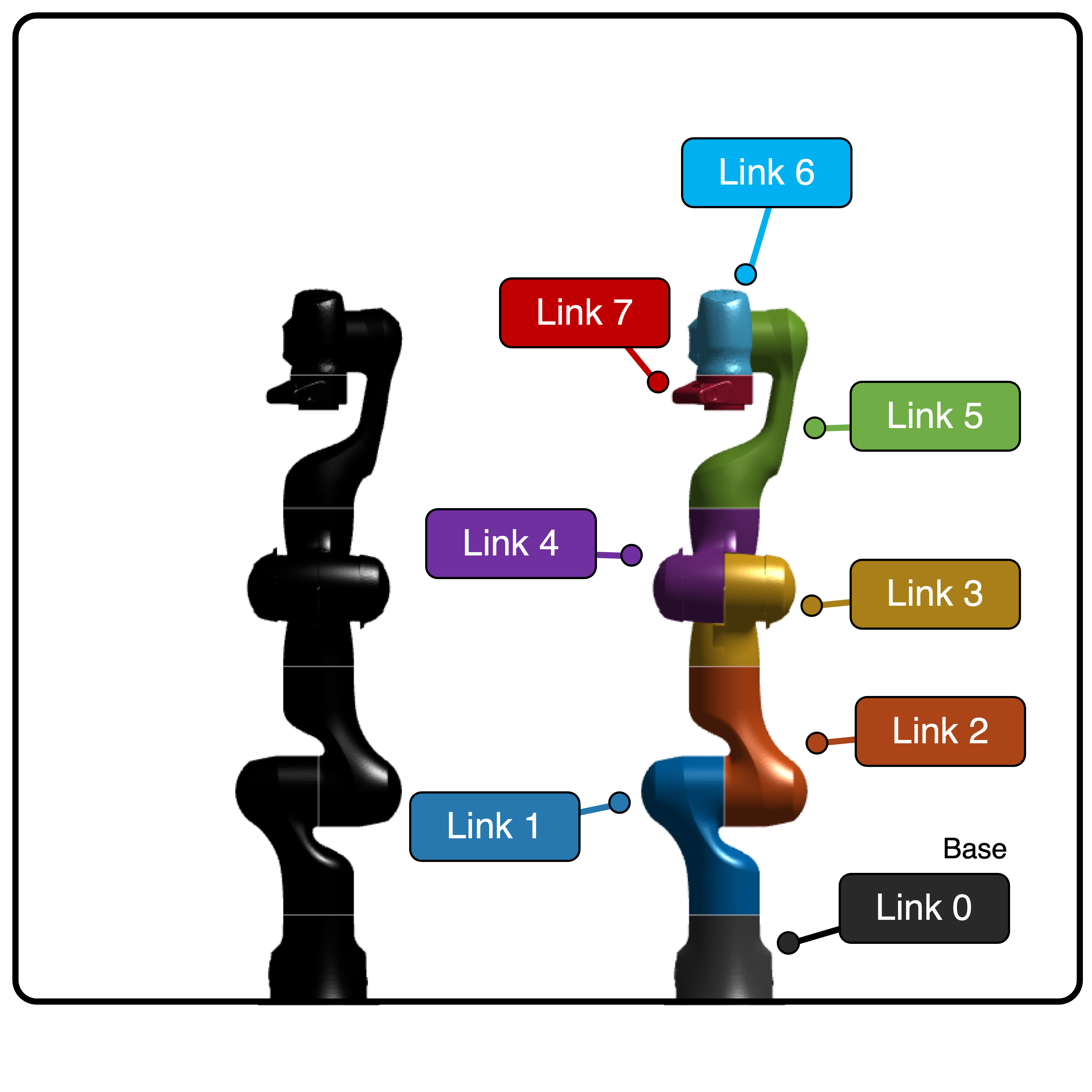
The Franka Emika Robot is a kinematically redundant robot with 7 DOF. The links and the fixed base of the robot are shown below.
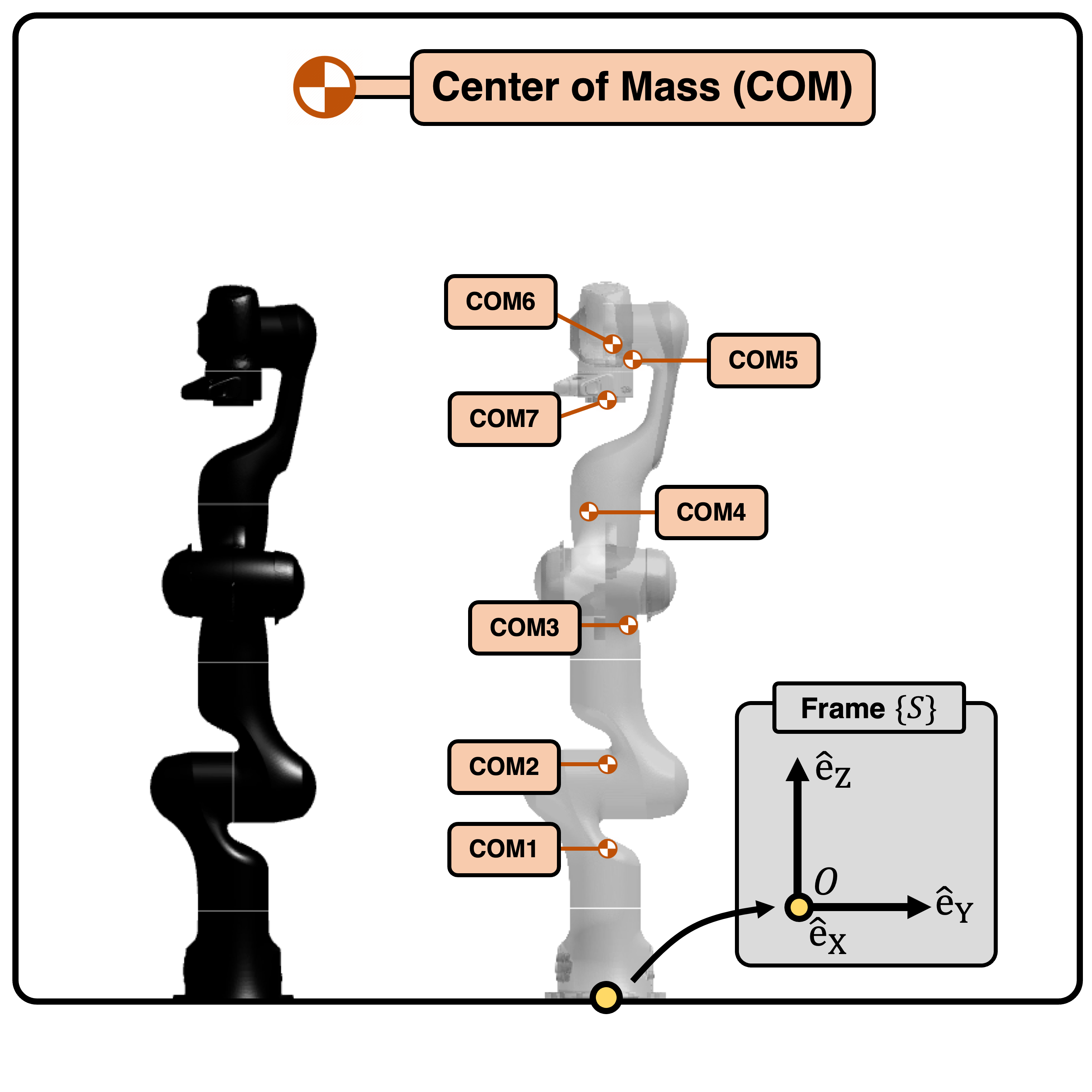
The Locations of Center of Mass (CoM)
The CoM locations of the 7 links are depicted below.
Center of Mass |
Center of Mass Locations (m) |
Mass (kg) |
|---|---|---|
COM1 |
(0.0039, 0.0021, 0.2394) |
4.9707 |
COM2 |
(-0.0031, 0.0036, 0.3618) |
0.6469 |
COM3 |
(0.0275, 0.0392, 0.5825) |
3.2286 |
COM4 |
(0.0293, -0.0275, 0.7534) |
3.5879 |
COM5 |
(-0.0120, 0.0410, 0.9946) |
1.2259 |
COM6 |
(0.0601, 0.0105, 1.0189) |
1.6666 |
COM7 |
(0.0883, 0.0021, 0.9339) |
1.4655 |
Note that the CoM locations are all expressed with respect to frame \(\{S\}\). The values are derived from Figure 4 in this reference. The detailed derivation of these values are shown in this post.
Initial Configuration and Joint Parameters
Below, the robot in initial configuration with stationary coordinate frame \(\{S\}\) and origin \(\{O\}\) is shown:
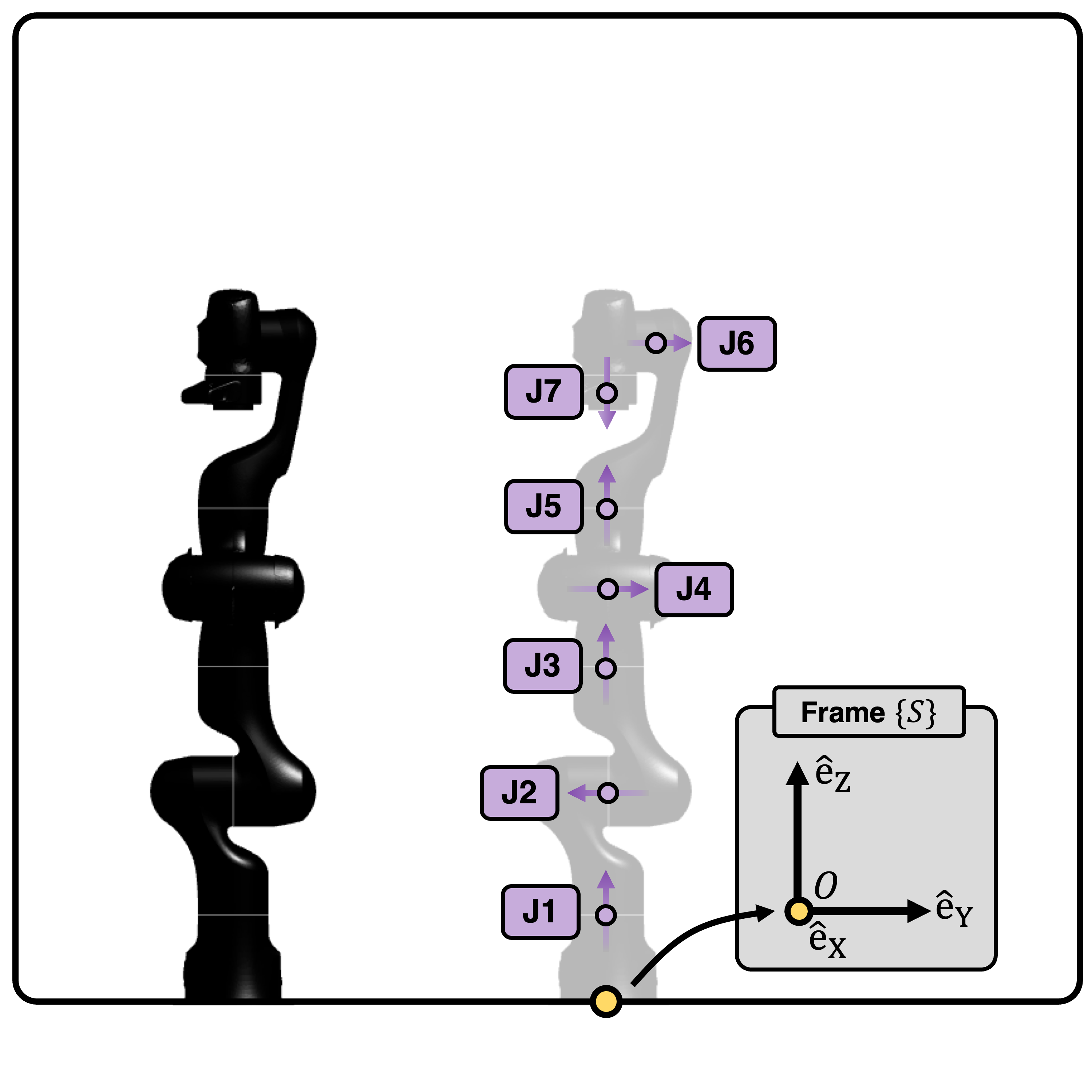
Joint |
Type |
Point on Joint Twist Axis (m) |
Joint Direction |
Joint Twist |
|---|---|---|---|---|
J1 |
Rev. (1) |
(0, 0, 0.3330) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1) |
J2 |
Rev. (1) |
(0, 0, 0.3330) |
(0, -1, 0) |
(0.333, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0) |
J3 |
Rev. (1) |
(0, 0, 0.6490) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1) |
J4 |
Rev. (1) |
(0.0825, 0, 0.6490) |
(0, 1, 0) |
(-0.649, 0, 0.0825, 0, 1, 0) |
J5 |
Rev. (1) |
(0, 0, 1.0330) |
(0, 0, 1) |
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1) |
J6 |
Rev. (1) |
(0, 0, 1.0330) |
(0, 1, 0) |
(-1.0330, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0) |
J7 |
Rev. (1) |
(0.0880, 0, 1.0330) |
(0, 0, -1) |
(0, 0.0880, 0, 0, 0, -1) |
Here, “Rev.”” stands for revolute joint.
Inertia Tensor of each Linkage
Given axes \(\hat{e}_x\), \(\hat{e}_y\), \(\hat{e}_z\), the inertia matrices of the links about the CoM, \(I_i\) are shown below:
|
\[\begin{split}I_{1} = \begin{bmatrix}
\phantom{-}0.7470 & -0.0002 & 0.0086 \\
-0.0002 & \phantom{-}0.7503 & 0.0201 \\
\phantom{-}0.0086 & \phantom{-}0.0201 & 0.0092
\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]
|
|
\[\begin{split}I_{2} = \begin{bmatrix}
0.0085 & \phantom{-}0.0103 & \phantom{-}0.0040 \\
0.0103 & \phantom{-}0.0265 & -0.0008 \\
0.0040 & -0.0008 & \phantom{-}0.0281
\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]
|
|
\[\begin{split}I_{3} = \begin{bmatrix}
\phantom{-}0.0565 & -0.0082 & -0.0055 \\
-0.0082 & \phantom{-}0.0529 & -0.0044 \\
-0.0055 & -0.0044 & \phantom{-}0.0182
\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]
|
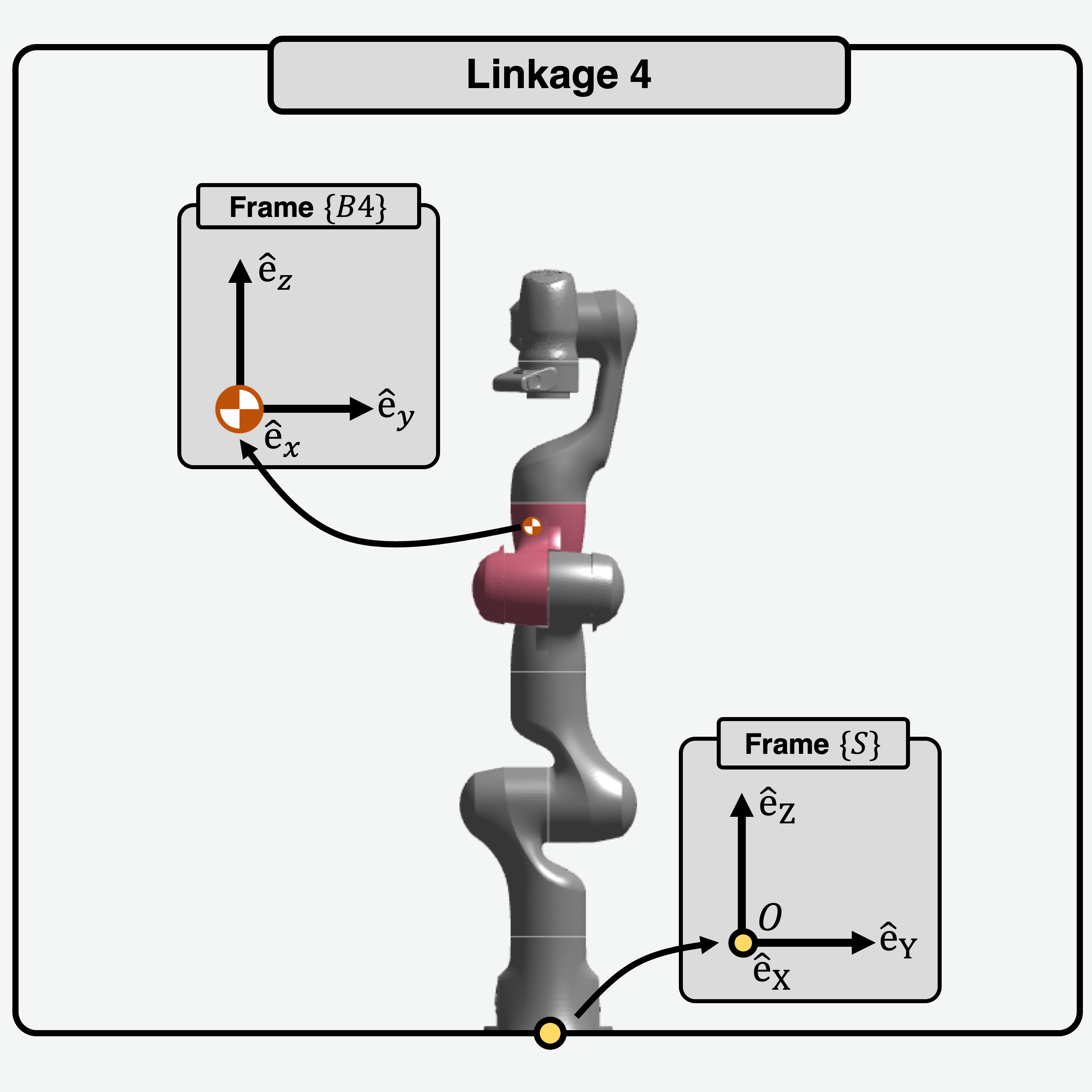
|
\[\begin{split}I_{4} = \begin{bmatrix}
\phantom{-}0.0677 & -0.0039 & 0.0277 \\
-0.0039 & \phantom{-}0.0776 & 0.0016 \\
\phantom{-}0.0277 & \phantom{-}0.0016 & 0.0324
\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]
|
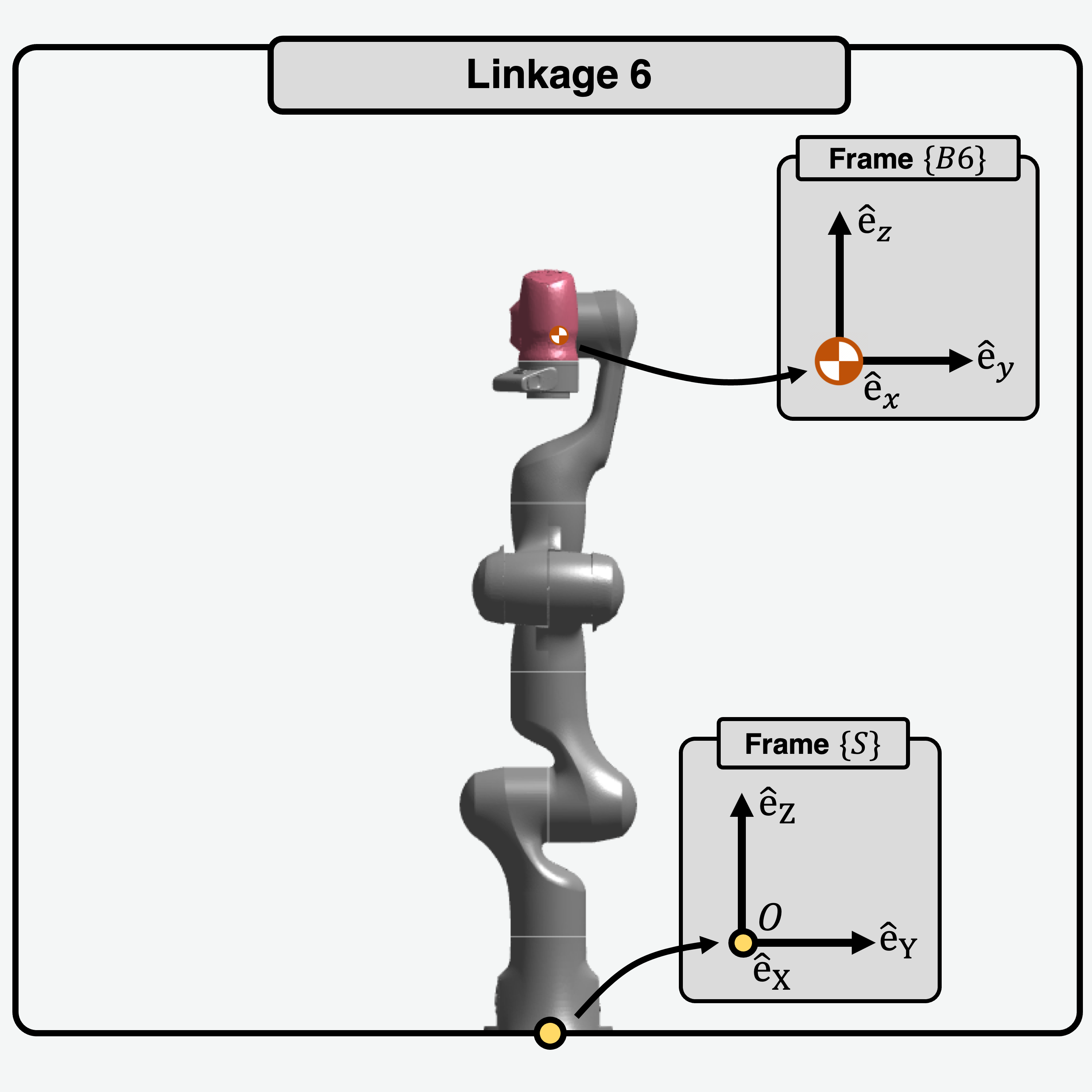
|
\[\begin{split}I_{6} = \begin{bmatrix}
0.0025 & \phantom{-}0.0001 & \phantom{-}0.0015 \\
0.0001 & \phantom{-}0.0118 & -0.0001 \\
0.0015 & -0.0001 & \phantom{-}0.0106
\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]
|
The values are derived from Figure 4 of this reference. The detailed derivation of these values are shown in this post.
Example Exp[licit]-MATLAB
To construct a Franka robot in Exp[licit]-MATLAB, run the following code:
% Construct Franka object, with high visual quality
robot = franka( );
robot.init( );
% Set figure size and attach robot for visualization
anim = Animation( 'Dimension', 3, 'xLim', [-0.7,0.7], 'yLim', [-0.7,0.7], 'zLim', [0,1.4] );
anim.init( );
anim.attachRobot( robot )
The output figure should look like this:
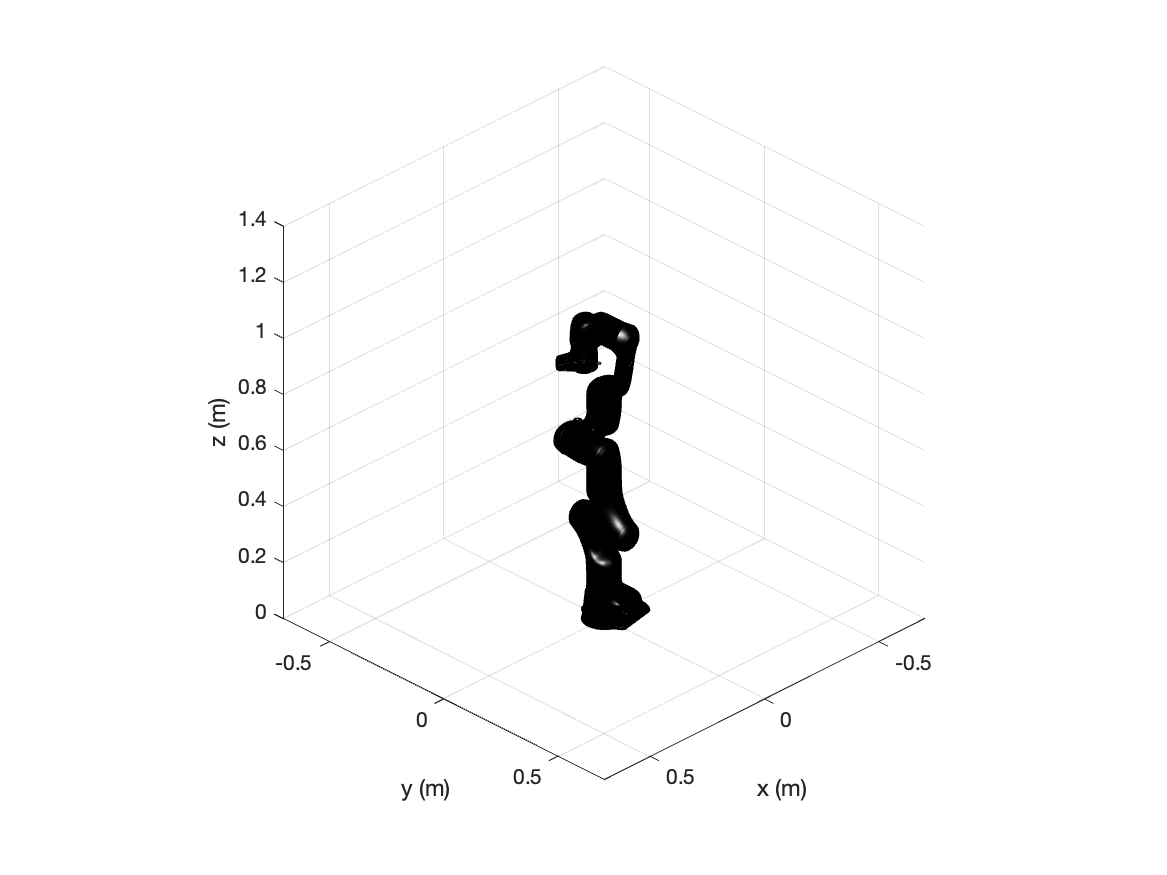
An example application for the Franka robot can be found under /examples/main_franka.m.